The Body Cavity That Is Enclosed by the Rib Cage
Cavity bounded primarily by the abdominal muscles and the superior bones fo the pelvis. The body cavity that is enclosed by the rib cage is known as the.

Thoracic Cavity Description Anatomy Physiology Britannica
The thoracic cavity contains the lungs and the heart which is located in the mediastinum.

. This also contains two compartments which are the mediastinum and two pleural cavitiesIn a mammal the. The body cavity surrounded by the hip bones is called the. Terms in this set Thoracic Cavity.
Human body cavities are separated by membranes and other structures. Shoulder and the elbow. Thoracic cavity also called chest cavity the second largest hollow space of the body.
The thoracic cavity is the more superior subdivision of the anterior cavity and it is enclosed by the rib cage. It is enclosed by the ribs the vertebral column and the sternum or breastbone and is separated from the abdominal cavity the bodys largest hollow space by a muscular and membranous partition the diaphragm. The organs found in the thoracic cavity can be classified according to the systems to which they belong.
Small space enclosed by the bones of the pelvis. Whereas the peritoneal cavity is the potential space between the visceral and parietal peritoneum. The term arm in anatomy refers to the region between the.
The body cavity that is enclosed by the rib cage is. The diaphragm forms the floor of the thoracic cavity and separates it from the more inferior abdominopelvic cavity. Cavity surrounded by the rib cage bounded inferiorly by the diaphragmand divided into right and left parts by the mediastinum.
Thoracic cavity also called chest cavity the second largest hollow space of the body. The two largest human body cavities are the ventral cavity and dorsal cavity. The diaphragm forms the floor of the thoracic cavity and separates it from the more inferior abdominopelvic cavity.
The term arm in anatomy refers to the region between the. It houses the primary organs of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems such as the heart and lungs but also includes organs from other systems such as the esophagus and the thymus gland. The thoracic wall or rib cage is sometimes called thoracic cage.
If a hairline fracture occurred in the proximal humerus arm bone would the injury bed _ Why. Thoracic Cavity is the second largest hollow space in the body that is enclosed by the ribs. The body cavity surrounded by the hip bones is called the.
The thoracic cavity also known as the chest cavity is a cavity enclosed by the ribs the vertebral column and the sternum or the breastbone. The chest cavity is bound by the thoracic vertebrae which connect to the ribs that surround the cavity. It houses the lungs and the bronchi part of the oesophagus and trachea as well as the heart and major blood vessels.
The thoracic cavity protects many organs that are vital to the functioning of the body and even life. The term leg in anatomy refers. A muscular and membranous partition the diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity.
The thoracic cavity is the anterior ventral body cavity found within the rib cage in the torso. The thoracic cavity is actually composed of three spaces each lined with mesothelium a special film-like tissue that. The body cavity that is enclosed by the rib cage is known as the CAN EXERCISE ONE Organs Systems and Organization of the Body 27.
The thoracic cavity contains the lungs and the heart which is located in the mediastinum. It is enclosed by the ribs the vertebral column and the sternum or breastbone and is separated from the abdominal cavity the bodys largest hollow space by a muscular and membranous partition the diaphragm. A mitochondrion belongs to which level of organization.
A body cavity is a fluid-filled space inside the body that holds and protects internal organs. The human body like that of many other multicellular organisms is divided into a number of body cavities. The abdominal cavity is the entire cavity enclosed by the rib cage abdominal muscles vertebral column diaphragm and pelvic inlet.
The specific body cavity that is enclosed by the rib cage is known as the. The thoracic cavity is the more superior subdivision of the anterior cavity and it is enclosed by the rib cage. The body cavity surrounded by the hip bones is called the.
In a clinical report there is a note of a laceration cut on the posterior crural region. The thoracic cavity also called the chest cavity is a cavity of vertebrates bounded by the rib cage on the sides and top and the diaphragm on the bottom.

Thoracic Cavity Definition Organs Of Chest Cavity Biology Dictionary

Pin By Kacho Zom On Nclex Thoracic Cavity Valsalva Maneuver Heart Problems

Thoracic Cavity Description Anatomy Physiology Britannica

The Vertebral Column As A Whole Human Anatomy Rib Cage Drawing Anatomy For Artists Thoracic Cage

The Thoracic Cage The Ribs And Sternum Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141
Dorsal And Ventral Body Cavities Open Educational Resource Oer Unsyiah Library

Lungs Diagram How Do We Breathe Lungs And Pleura Interactive Biology By Leslie Lung Anatomy Respiratory System Anatomy Human Lungs

Vertebral And Sternal Articulations Of A Typical True Rib Human Anatomy And Physiology Psychology Books Anatomy Bones

Pin By Zero Rayner On Skeletal System Rib Bones Human Ribs Anatomy Bones
Tampilan Petugas Dorsal And Ventral Body Cavities

Figure 8 5 Base Of The Skull A Inferior View Fa Internal View Of The Cranial Floor Hypoglossal Nerve Sphenoid Bone Internal Carotid Artery
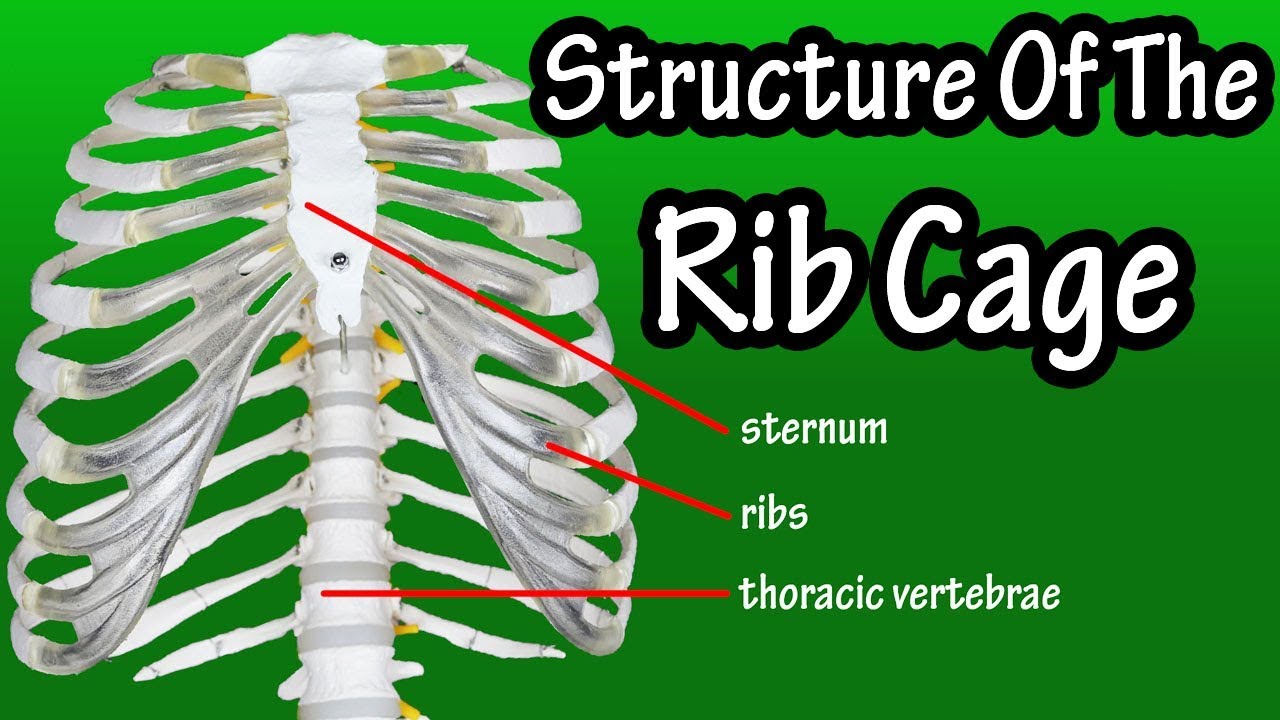
Structure Of The Rib Cage How Many Ribs In Human Body What Is The Sternum Youtube

Ribs Anatomy Types Ossification Clinical Significance How To Relief Human Ribs Human Body Anatomy Rib Cage Anatomy

Anterior View Of The Skeleton Of The Thoracic Cage Human Ribs Human Body Anatomy Rib Cage Anatomy

Figure 8 11 The Sphenoid Bone A Superior View Fa Posterior View Sphenoid Bone Bones Medical Anatomy




Comments
Post a Comment